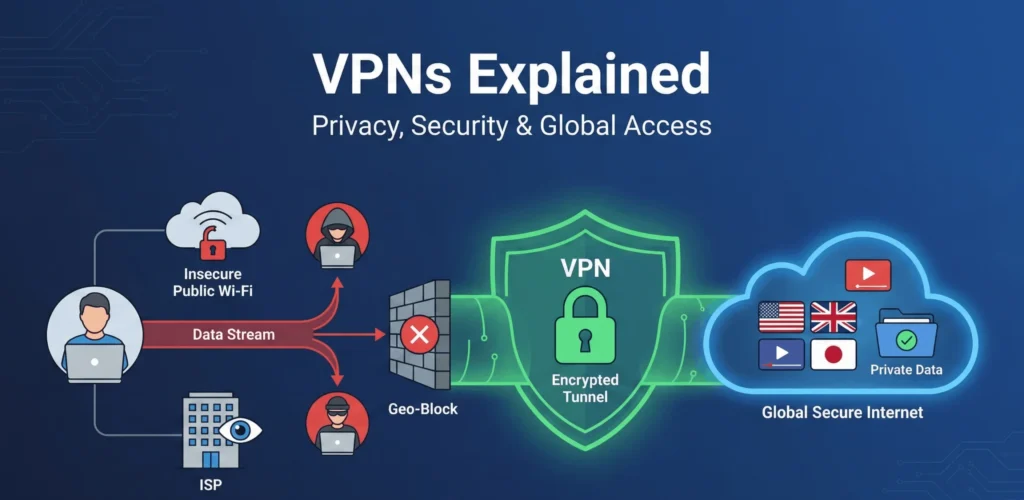
Your ISP, advertisers, and even hackers can monitor your online actions unless you use a VPN. In this guide, we explain how Virtual Private Networks protect your online activity and why they are essential for modern internet users.
A virtual private network (VPN) is a crucial tool for protecting data and ensuring online anonymity. This article explains how VPNs operate, outlines the types available, and describes why using a VPN can benefit your online activities.
Table of Contents
What Is a VPN and How Does It Work?
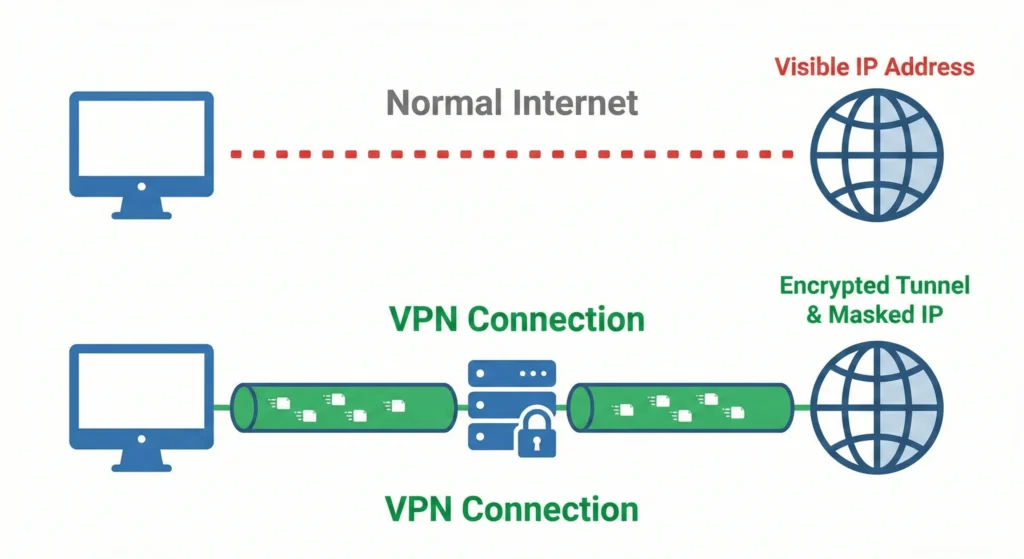
A VPN stands for virtual private network, a secure VPN service that creates an encrypted connection over the internet. When you connect to the VPN, your internet traffic is routed through a remote VPN server run by a VPN provider. This server, run by a VPN, effectively masks your IP address and encrypts your data, ensuring that your traffic is unreadable to third parties.
The process begins when a VPN client (the VPN app on your device) establishes a VPN connection to a VPN server. Essentially, the VPN acts as a middleman, ensuring that only your device and the VPN server understand the data.
VPN Protocol: The Backbone of Your Security
A VPN protocol consists of the rules that govern the interaction between the computer and the VPN. These protocols are essential to how VPNs work, ensuring a stable VPN connection. When choosing a VPN, you will find that different VPN providers offer various options:
- OpenVPN: A popular open-source VPN protocol known for its reliability.
- WireGuard: A modern VPN protocol offering faster speeds.
- IKEv2/IPsec: This protocol is particularly well-suited for mobile VPNs, as it keeps your connection stable when switching between Wi-Fi and cellular data networks.
How VPNs Protect Your Privacy
A VPN protects you by creating a VPN tunnel for your internet connection. When you use VPN software, it hides your IP address and replaces it with the IP address of the remote VPN server. This makes it difficult for your ISP (internet service provider) to browse your history or track your VPN use.
A reliable VPN is vital on public Wi-Fi networks, which are often unsecured. VPNs protect your data from hackers and block ISP throttling, so you maintain connection speed during gaming or streaming. Learn more about VPNs on Wikipedia.
Different Types of VPNs: Which One Do You Need?
Let’s take a closer look at the different types of VPNs and help you identify which one best suits your needs. Understanding the types of VPNs is crucial when choosing a VPN for your specific use case. While they all encrypt internet traffic, their architectures differ:
- Remote Access VPNs let individuals securely connect to corporate or private networks from remote locations, which is essential for remote workers.
- Site-to-Site VPN: Unlike a personal VPN, this classic setup connects entire offices or locations. This lets people in different locations securely share resources as if they were on a single local network.
- Mobile VPNs handle shifting connections on your device, ensuring the VPN stays active between Wi-Fi and cellular data.
How to Choose the Right VPN: A Buyer’s Guide to Digital Sovereignty
Selecting a VPN provider is a critical decision for your cybersecurity infrastructure. You shouldn’t just pick the first service you see; instead, evaluate the provider based on these four pillars of online anonymity and performance.
1. Military-Grade Encryption and Advanced Protocols
To keep your data packets unreadable to hackers, your VPN should use AES-256 encryption. This is the standard for end-to-end protection. Also, ensure the provider supports current tunneling protocols that balance speed and security:
- WireGuard: The current industry standard for the best balance of throughput and connection stability.
- OpenVPN: A highly versatile, open-source protocol known for bypassing tough firewalls and providing a secure gateway.
- IKEv2/IPsec: Excellent for mobile users who need a seamless handoff between Wi-Fi and cellular data.
2. The “Privacy Stack”: Kill Switch and Leak Protection

A standard encrypted connection isn’t always enough to stop your actual IP address from leaking. That’s why a premium VPN should provide a strong ‘Privacy Stack,’ which is a combination of tools and features that protect your identity online:
- Network Kill Switch: This acts as a failsafe, instantly halting all internet traffic if the VPN tunnel drops, ensuring your real IP address is never exposed.
- Split Tunneling: This feature lets you send important traffic (like banking data) through the VPN for security, while allowing low-risk apps (such as your local weather app) to use your regular internet connection.
- DNS Leak Protection: DNS stands for Domain Name System, which translates web addresses into numbers your device can connect to. This feature makes sure those translations stay private and aren’t visible to your ISP, so your browsing history isn’t accidentally leaked.
3. Jurisdiction and Audited No-Logs Policy
Your digital footprint is only as safe as the laws governing your provider. Look for a service headquartered in a privacy-friendly jurisdiction outside the 5/9/14 Eyes Alliances.
- Pro Tip: A “No-Logs” claim is only credible if verified by an independent third-party audit (by firms like PwC or Deloitte). This demonstrates that the provider stores no connection or traffic logs.
4. Global Server Network and Obfuscated Traffic
If your goal is to bypass geo-restrictions or access global streaming libraries, look for a large server fleet.
- Server Diversity: A high server count prevents network congestion, maintaining fast speeds even during peak hours.
- Obfuscated Servers (Stealth VPN): These are special servers that disguise VPN traffic to look like regular, secure web traffic (HTTPS). This is important in countries or regions where governments or networks try to block VPNs using methods like Deep Packet Inspection (DPI), which examines internet traffic in detail.
Free VPN vs. Paid VPN: What’s the Difference?
Once you’ve considered provider features, it’s important to weigh whether to choose a free or paid VPN. Here are the key differences between the two options.
When searching for a VPN, you’ll see both free and paid versions. A free VPN can seem attractive, but it often comes with data limits or slower speeds. Some free services may even monetize your data. By contrast, paid VPNs like Proton VPN provide a strict no-logs policy and robust security. Ultimately, a VPN is a wise investment if you value lasting protection.
Read More: Top VPN Providers Lumolog Compared
Key Factors for the Right VPN
- Speed: A good VPN should not significantly slow your internet connection.
- Kill Switch: A vital VPN feature that cuts the internet if the VPN connection drops.
- Multi-Device Support: Ensure the VPN app works on all your devices.
Benefits of Using a VPN: Why Every Modern User Needs a VPN
Beyond security, a VPN opens access to a borderless internet. By creating a secure tunnel, you control how websites view you and how you access global content.
1. Bypassing Geo-Restrictions and “Digital Borders.

Many streaming services and news outlets use geo-blocking to restrict access based on your physical IP address. A VPN allows you to bypass these barriers by “teleporting” your connection to a remote server.
- Global Content Access: When you connect to a server in another country, the website identifies you as a local user. This is essential for travelers who need access to their home streaming libraries or for users wanting to explore international content.
- Streaming Optimization: High-quality VPNs ensure you can enjoy 4K content without the “proxy error” messages often associated with lower-tier services.
2. Snagging Better Deals with Price Discrimination Hacks
Airlines, hotel booking sites, and even some e-commerce platforms use dynamic pricing. They track your location and browsing history to show you different prices.
- Location Spoofing: By switching your VPN server to a different country or city, you can compare prices and often find significantly cheaper flights or car rentals.
- Avoiding Tracking Cookies: Because a VPN masks your identity, sites find it harder to “push” prices higher based on your repeated visits to their pages.
3. Preventing Bandwidth Throttling
Is your internet speed suddenly dropping while you’re watching a movie? This is often ISP Throttling. Your Internet Service Provider identifies high-bandwidth activities and slows your connection to save network resources.
- The Solution: Because a VPN encrypts your traffic, your ISP can no longer see what you are doing (streaming vs. browsing). Without that visibility, they cannot trigger automated speed reductions, ensuring you get the performance you actually pay for.
4. Protecting Your Privacy from ISP Data Mining
In many regions, ISPs are legally permitted to track your browsing habits and sell that metadata to advertisers. Using a VPN ensures that your online history remains private. Your ISP will only see that you are connected to an encrypted VPN server, effectively cutting off their ability to harvest and sell your digital footprint.
How to Install and Configure Your VPN: Step-by-Step Guide
Setting up a VPN is straightforward, but ensuring it is configured for maximum privacy requires attention to detail. Follow these steps to secure your device in minutes:
Step 1: Select and Subscribe to a Reputable VPN Provider
Before installing software, you must choose a provider that fits your needs (Remote Access, Mobile, or Site-to-Site).
- Pro Tip: Look for providers that offer a Strict No-Logs Policy and have been independently audited. Avoid “free” services that may compromise your data integrity.
Step 2: Download the Official VPN Client
Navigate to the provider’s official website or your device’s native App Store (iOS/Android).
- Security Note: Always download the client software directly from the source to avoid “repackaged” apps that might contain malware or tracking scripts.
Step 3: Install and Authenticate The VPN
Launch the installer and follow the on-screen prompts. Once installed, open the application and log in using your secure credentials.
- Optimization: Most modern VPN apps let you choose your preferred VPN Protocol (such as WireGuard or OpenVPN) in the settings menu.
Step 4: Establish a Secure Connection With VPN
Select a VPN server location from the available global list. For the fastest speeds, choose a server physically closest to you. Click “Connect” and wait for the server handshake to complete, usually indicated by the app interface turning green or showing a “Protected” status.
Step 5: Perform a VPN Connection Audit (The Verification)
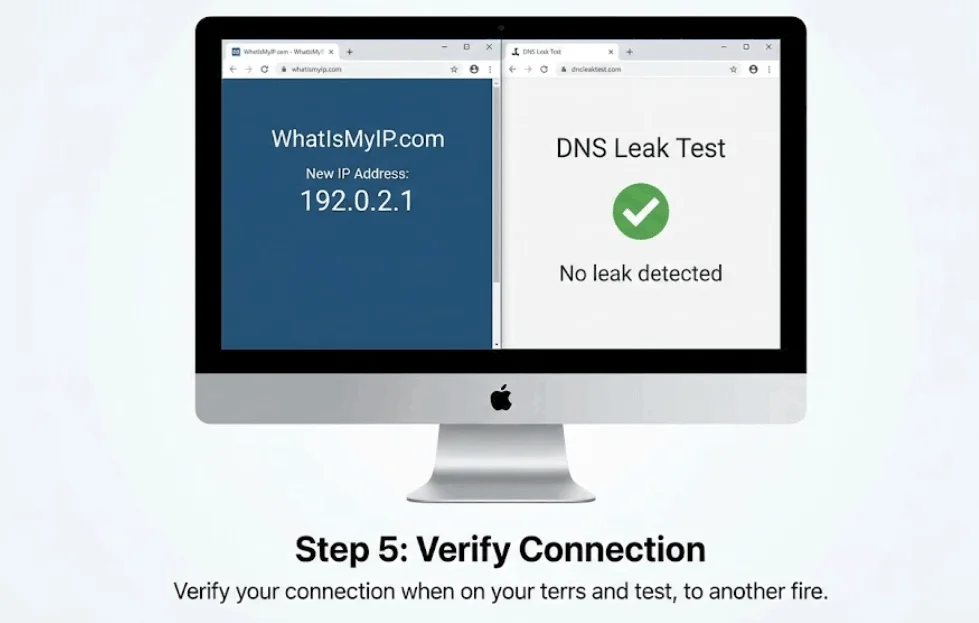
Never assume you are protected just because the app is “On.” Verify your anonymity by:
- Checking Your IP: Visit a site like WhatIsMyIP.com to ensure the location matches that of your VPN server, not your physical location.
- Running a DNS Leak Test: Ensure your DNS queries aren’t leaking to your ISP through the encrypted tunnel.
- Activating the Kill Switch: Ensure this feature is enabled in the settings to prevent data exposure if the connection drops.
Starting Your VPN Journey: Tips for First-Time Users
For first-time users, starting your VPN journey can seem daunting, but it’s actually quite simple. Begin by selecting a reputable VPN provider that aligns with your needs. Once you have chosen a VPN, familiarize yourself with the VPN app’s interface and settings. Start by connecting to a VPN server in your own country to minimize latency and ensure a stable VPN connection while using the VPN to enhance your online security. Several features can enhance your experience as you learn:
- The kill switch automatically disconnects your internet connection if the VPN connection drops.
- Access geo-restricted content from different server locations and further enhance your privacy.
A good VPN should offer helpful resources and customer support to guide you along the way. It’s a smart choice to use a VPN from the beginning.
Common Misconceptions About VPNs
Starting a VPN journey can feel confusing because of many myths. Let’s look at what a VPN really does compared to what people think.
- Myth: A VPN makes you 100% anonymous. Reality: A VPN masks your IP address and hides your activity from your ISP, but it does not make you a “ghost.” Websites can still track you even if you log in to your accounts (like Google or Facebook) or if they use “cookies.” A VPN alone is just one part of your privacy plan.
- Myth: Using a VPN is illegal. Reality: In most countries, you can legally use a VPN service to protect your data. Businesses and individuals use them every day for safety. However, a VPN won’t protect you from the law if you use it for illegal activities, such as hacking.
- Myth: Free VPNs are just as good as paid ones. Reality: In the VPN vs free proxy debate, the paid VPN almost always wins. Free VPNs often have slow speeds, limited data, and might even sell your browsing history to advertisers. A paid VPN invests in better security and faster servers.
- Myth: A VPN will ruin your internet speed. Reality: While the encryption process takes a little time, a good VPN will not noticeably slow you down. Modern technology ensures your VPN journey remains fast and smooth.
Virtual Private Networks (VPNs) FAQs
1: Is Using a VPN Legal?
In the United States and most democratic nations, using a VPN is 100% legal. VPNs are legitimate tools used by corporations and individuals to secure data. However, while the tool is legal, using it to facilitate illegal acts, such as copyright infringement, cyberstalking, or accessing illicit marketplaces, remains a crime. Always check local regulations if you are traveling to “Internet-restricted” countries like China, Russia, or Iran.
2: Can Netflix Ban My Account for Using a VPN?
It is highly unlikely that Netflix will ban your account for using a VPN, but they may geo-block your access. Netflix’s Terms of Service discourage bypassing regional content restrictions. If their system detects a known VPN IP address, you will typically see a “proxy error” rather than a total account ban. To resolve this, premium users typically switch to a server optimized for streaming.
3: How Do VPNs Circumvent Digital Censorship?
VPNs bypass firewalls by using a process called tunneling. By connecting to a remote server in a country with an open internet, your traffic originates from that location rather than your local, restricted network. In high-censorship environments, look for providers that offer Obfuscation (Stealth VPN), which masks VPN traffic as standard HTTPS traffic to avoid Deep Packet Inspection (DPI).
4: Does a VPN Hide Torrenting Activity from My ISP?
Yes, a VPN hides P2P (Peer-to-Peer) activity from your Internet Service Provider (ISP) by encrypting the traffic. Without a VPN, your ISP can see that you are downloading BitTorrent files and may issue a DMCA notice or throttle your bandwidth. A VPN with a No-Logs Policy ensures that even if an ISP or third party requests your data, there is no record of your downloads to provide.
5: VPN vs Incognito Mode: What is the Difference?
These two tools solve different privacy problems and are most effective when used together.
1: Incognito Mode: Provides only local privacy, which is a key reason many people choose VPN services. It prevents your browser from saving history, cookies, and form data on your specific device.
2: VPN: Provides network privacy. It encrypts your data and hides your IP address from the websites you visit and your ISP.
6: Can a VPN Provide 100% Anonymity?
No, a VPN provides privacy, not total anonymity. While it masks your IP address, you can still be identified through browser fingerprinting, tracking cookies, or if you are logged into accounts like Google or Facebook. For maximum anonymity, advanced users often chain a VPN with the Tor Browser to add multiple layers of encryption and node-routing.
7: What is a VPN Kill Switch and Why Do I Need It?
A Kill Switch is a critical security feature that acts as a failsafe. If your VPN connection drops unexpectedly, the Kill Switch instantly disconnects your device from the internet. This prevents your “naked” IP address and unencrypted data from being exposed to the public web for even a split second.
he Bottom Line: Taking Control of Your Digital Footprint
In an era of increasing surveillance and data breaches, a VPN is no longer just a luxury for the tech-savvy; it is a fundamental requirement for anyone serious about their online privacy. By masking your IP address and enforcing end-to-end encryption, a Virtual Private Network shifts the power back into your hands, allowing you to browse, stream, and communicate without being a target for trackers or hackers.
However, remember that a VPN is only one piece of the puzzle. For true digital sovereignty, you must combine a high-quality VPN with strong password habits, two-factor authentication, and a critical eye for the sites you visit.