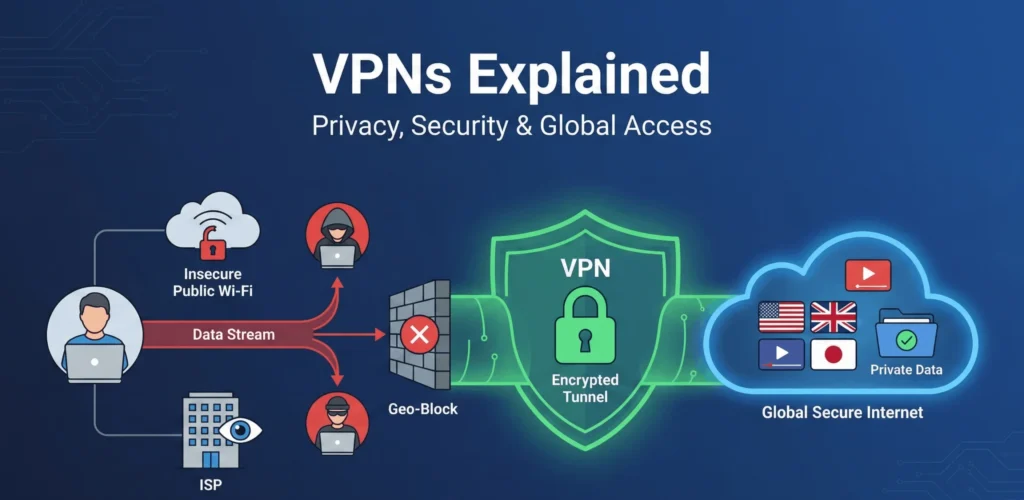
In today’s digital healthcare environment, secure remote access to Mount Sinai systems is essential for healthcare professionals, students, and staff. The Mount Sinai VPN enables you to securely access essential resources, patient data, and internal networks from anywhere. Whether you are a doctor accessing patient records remotely, a student reviewing coursework, or staff using the employee portal, understanding how to use the Mount Sinai VPN helps you stay productive and secure.
This guide explains Mount Sinai VPN access, from setup to troubleshooting. It addresses common issues such as login problems and connection timeouts. By the end, you will know how to connect securely, resolve basic issues yourself, and maintain the safety of healthcare data.
Table of Contents
What is Mount Sinai VPN?
The Mount Sinai VPN (Virtual Private Network) lets approved users access Mount Sinai’s internal resources from outside the hospital. It establishes a secure, encrypted connection between your device and the hospital network, ensuring the safe storage of healthcare data.
Mount Sinai VPN provides access to essential healthcare tools, including Meditech HIS, electronic health records, email, and clinical databases. This secure link enables healthcare professionals to work from anywhere while utilizing the necessary tools for patient care.
Employees, students, and other approved users benefit from the Mount Sinai VPN. Medical staff can access patient information securely from anywhere, ensuring continuity of care even when working remotely. Faculty and students can access academic and research resources, and administrative staff can utilize HR systems and communication tools with confidence.
The system utilizes robust security measures to meet healthcare standards and comply with HIPAA regulations. It includes two-factor authentication, data encryption, and other protections against unauthorized access. All data sent between your device and the Mount Sinai network stays encrypted and safe.
You can use Mount Sinai VPN on most modern devices, including Windows, Mac, iOS, and Android. You will need a stable internet connection for optimal performance and uninterrupted access to hospital systems.
Related Reading: VPNs Explained: What Are They & Why Use a VPN?
Mount Sinai VPN Login: Step-by-Step Guide
Successfully logging into the Mount Sinai VPN requires proper preparation and following specific steps to ensure secure authentication.
Before you connect, make sure you have your network ID, password, and the Symantec VIP Access app for two-factor authentication.
Your device should also have the Mount Sinai VPN client software installed and properly configured.
Desktop Login Process
To start the desktop login for Mount Sinai VPN, first launch the VPN client software on your computer. Locate the VPN application in your Programs folder or System Tray, and double-click it to open. The client interface will display connection options and fields for entering your credentials.
- Accessing the VPN Client: When the app opens, you’ll see the main connection screen. Select the appropriate Mount Sinai server from the dropdown menu if multiple options are available. The interface should display fields for username, password, and authentication method.
- Entering Credentials: Type your Mount Sinai network ID in the username field. This is usually your employee ID or student ID number. Enter your network password in the designated password field. If prompted for domain information, use the Mount Sinai domain as specified in your IT documentation.
- Two-Factor Authentication: Most Mount Sinai VPN setups need two-factor authentication with Symantec VIP Access. Open your VIP Access app on your mobile device and generate a security code. Enter this VIP security code in the appropriate field within the VPN client interface.
- Connection Verification: Click the connect button and wait for the authentication process to complete. A successful connection typically displays a green indicator or a connected status message. To verify your connection, try accessing internal Mount Sinai resources. You can also check your IP address to see if it matches the IP address of the hospital network.
Accessing Webmail After VPN Login
Once you’ve successfully connected to the VPN, you’ll be presented with a landing page displaying various internal resource links. Look for the Webmail section, typically marked with an envelope icon or labeled as “Webmail.”
Simply click this link, and your default browser will open your secure email dashboard. You can now check your messages, send files, and manage your communications just as you would from within the hospital network.
If prompted, enter your regular network credentials and complete two-factor authentication to ensure continued security as you access your mailbox.
Mobile Device Login (iOS and Android)
To access the Mount Sinai VPN on a mobile device, use the dedicated apps available in official app stores. Download the recommended VPN client app as specified by Mount Sinai IT Services.
The mobile login process uses similar steps for authentication. However, the interface may differ based on the platform.
For iOS devices, launch the VPN app and navigate to the connection settings. Enter your Mount Sinai credentials and complete two-factor authentication using your VIP Access app.
Android devices work similarly, but menu locations and interface elements can vary slightly between app versions.
Web Browser Login Alternative
Some users can access a web-based VPN portal. This lets them connect using a browser.
This SSL VPN connection method offers a solution for devices that can’t install client software. Use your web browser to access the Mount Sinai VPN portal. Simply enter the URL provided by IT services and follow the prompts to authenticate.
Initial VPN Setup and Installation
Setting up your Mount Sinai VPN right from the start helps you connect easily. It also reduces future connection problems. The installation process depends on your operating system and device type. But if you follow these steps, you’ll set up secure remote access correctly.
System Compatibility Check
Before setting up the Mount Sinai VPN, verify that your device meets the minimum system requirements. Windows users should have Windows 10 or later, while Mac users need macOS 10.12 or newer versions. Mobile devices need iOS 12 or later, or Android 8.0 or later. This ensures the best compatibility with the VPN client software.
Check your storage space. Ensure you have sufficient space for the VPN app and its associated files. Most VPN clients need 50 MB to 200 MB of free space. This amount may vary depending on the software package. Check that your internet connection is stable. Ensure it has sufficient bandwidth for a reliable VPN connection.
Downloading the VPN Client
- Official Download Sources: Always get the Mount Sinai VPN client software from Mount Sinai IT Services. Avoid third-party sites or unofficial links. They may have harmful software or outdated versions that can compromise your security. If you’re unsure where to download, contact the Mount Sinai IT helpdesk.
- Version Recommendations: Install the latest version of the VPN client software from Mount Sinai IT. Newer versions typically include security updates, bug fixes, and improved compatibility with hospital networks. Keep a record of the version number for future reference and troubleshooting purposes.
Installation Process
The installation process may seem daunting, but with the right approach, you’ll have your VPN client up and running in just a few minutes. Whether you’re setting up on Windows, Mac, or mobile devices, these step-by-step instructions will guide you through each platform-specific requirement, ensuring a smooth installation that connects you securely to critical healthcare systems from day one.
Windows Setup: Download the Windows installer file. Then, right-click it and select “Run as Administrator” to obtain the necessary installation permissions. Follow the installation wizard prompts. Accept the default location unless you have specific needs. The installer might ask you to install extra network drivers or certificates.
During Windows installation, you might see User Account Control (UAC) prompts. These ask for permission to make system changes. Accept these prompts. They are required for the VPN client to install network components and establish a secure connection to the Mount Sinai Hospital network.
Mac Setup: Mac installation typically involves downloading a .dmg file or .pkg installer. Double-click the downloaded file and follow the macOS installation prompts. You may need to approve the installation in System Preferences > Security & Privacy if the software is from an identified developer outside the App Store.
macOS may request permission to add VPN configurations to your system. Grant these permissions. They’re crucial for the VPN client to set up secure network tunnels to Mount Sinai’s remote access servers.
Mobile App Installation: Install the suggested VPN app from the iOS App Store or Google Play Store. Search for the specific app name provided by Mount Sinai IT services, as generic VPN apps may not be compatible with the hospital’s network configuration. Avoid installing multiple VPN apps simultaneously, as they can conflict with each other.
Initial Configuration Settings
After installation, launch the VPN client and configure initial connection settings. Enter the Mount Sinai VPN server address. Choose your connection protocol and authentication methods from the IT documentation. Use your Mount Sinai credentials to create a connection profile. Save these settings for later use.
Configure automatic connection preferences based on your usage patterns. Healthcare pros who work remotely often like auto-connect settings. But occasional users may want to control their connections manually. Connect to your initial configuration. Then, check if you can access Mount Sinai resources.
Network Profile Setup
Make specific network profiles for different situations. This includes home office, mobile access, and public Wi-Fi connections.
Each profile can have custom settings. These are optimized for specific network environments and security needs. This approach ensures optimal performance and security regardless of your connection location.
Keep a record of your configuration settings. Ensure this information is secure but easily accessible later. Include server addresses.
- Add port numbers.
- Please note any special configuration requirements for your role or department at Mount Sinai Health System.
Advanced Configuration Options
Improving your Mount Sinai VPN setup can boost connection reliability, security, and speed. Advanced settings let experienced users customize their VPN for specific needs and networks. This also helps meet healthcare data protection standards.
Connection Protocols
Mount Sinai VPN supports various connection protocols. Each one has unique benefits for security and performance. OpenVPN offers robust security and performs well in various network configurations. This makes it a suitable choice for healthcare professionals who access patient data and clinical systems. IKEv2 performs well on mobile devices. It handles network changes smoothly. This makes it ideal for healthcare workers who frequently relocate between locations.
SSL VPN connections provide browser-based access. They work well in restrictive networks where traditional VPN protocols might be blocked. This option is ideal for using Mount Sinai systems on guest networks or public Wi-Fi, where standard VPN protocols may not function due to network restrictions.
Select the protocol that best suits your typical usage and network setup. Healthcare professionals who work from home may like OpenVPN for its strong security. In contrast, mobile healthcare workers might find IKEv2 helpful because it reconnects easily.
Split Tunneling Configuration
Split tunneling allows you to send specific traffic through the Mount Sinai VPN. Other internet traffic goes through your regular connection. This setup can boost performance. It reduces unnecessary strain on the hospital network. At the same time, it maintains secure access to electronic health records, Meditech HIS, and other sensitive systems.
Set up split tunneling to include Mount Sinai domains and IP ranges. This lets you browse the internet through your usual connection. This method keeps healthcare data secure and ensures great performance for non-clinical internet use.
Be cautious when using split tunneling in healthcare settings. If it’s not set up correctly, it may expose sensitive data or violate security rules. Ensure your split tunneling setup complies with Mount Sinai IT security rules and HIPAA regulations.
Auto-Connect Settings
Automatic connection features can simplify your workflow. They set up VPN connections when certain conditions are met. Set up auto-connect for untrusted networks. This keeps your connection to Mount Sinai systems safe when using public Wi-Fi or unfamiliar networks.
Create auto-connect rules for your home or office networks. This way, your device will automatically adjust its connection behavior. This smart automation streamlines the management of secure access to Mount Sinai’s remote systems. This enables seamless collaboration from various locations.
DNS Configuration
Correct DNS setup makes sure the domain name resolution works well with the Mount Sinai VPN. Set up your VPN client to use Mount Sinai DNS servers for internal domains. This way, you can still access external internet resources.
Custom DNS settings can boost connection reliability. They also help resolve internal Mount Sinai resources correctly. This setup is crucial for utilizing specialized healthcare apps and databases that rely on internal domain name resolution.
Bandwidth Optimization
Optimize bandwidth to ensure data-intensive applications run smoothly. This includes systems like medical imaging or large patient databases.
Set up compression settings and prioritize traffic. This will boost the efficiency of your Mount Sinai network connection.
Monitor bandwidth usage patterns and adjust settings according to your typical workload requirements. Healthcare professionals who frequently access large files or multimedia content may require different optimization settings to ensure optimal performance. This differs from users who mainly work with text and electronic health records.
Common Mount Sinai VPN Issues and Solutions
Users may encounter challenges connecting to the Mount Sinai VPN, even with the correct setup. Knowing common problems and their solutions helps you fix issues fast. This way, you can continue to access healthcare systems and resources effectively.
Connection Failures
Struggling to connect to the Mount Sinai VPN? From authentication errors to server timeouts, we’ll help you diagnose and fix common issues to get you back online quickly and securely.
Authentication Errors: Users often encounter authentication issues when accessing the VPN. If you see “authentication failed,” check that you’re using the right network ID and password. Remember that passwords are case-sensitive, and check that Caps Lock is not enabled.
Two-factor authentication problems often occur due to time synchronization issues with your Symantec VIP Access app. Check that your mobile device’s time and date settings are correct. Authentication codes depend on these settings and are time-sensitive. If the codes continue to fail, please contact the IT helpdesk. They can help resynchronize your VIP Access token.
Account lockouts can occur after multiple failed authentication attempts. If you think your account is locked, wait 15-30 minutes before trying again. You can also contact IT support for help. Avoid repeatedly trying incorrect credentials, as this can extend lockout periods.
Step-by-Step: Logging In to the VPN
- Open the VPN Portal. Click the appropriate link provided by your organization to launch the VPN login page.
- Enter your credentials. Use your Network ID as the username and your network password. Double-check for typos and ensure the password’s case matches.
- Open the Symantec VIP Access app on your mobile device.
- Enter the security code. The app generates a 6-digit security code that changes every 60 seconds. Input the current code into the “VIP Security Code” field on the login page.
- Click “Logon.” If successful, you’ll be directed to a webpage where you can access resources such as webmail or secure apps.
If you follow these steps and still experience issues, such as repeated authentication errors or trouble with the security code, review the troubleshooting tips above—or reach out to IT helpdesk for assistance. Taking care with each step can help you avoid common pitfalls and connect securely every time.
Server Timeout Issues: Connection timeout errors typically indicate issues with the network or the server. Check your internet connection. If you have multiple Mount Sinai VPN servers, try connecting to different ones to see if that resolves the issue. Temporary server maintenance or periods of high traffic can lead to timeout issues. These usually fix themselves.
Firewall or router configurations can cause timeout problems by blocking VPN traffic. If you’re on a home network, check your router’s firewall. Make sure it isn’t blocking VPN protocols and ports. Corporate networks may have additional restrictions that require IT assistance to resolve.
Network Connectivity Problems: DNS resolution issues can stop a proper connection. This can happen even if authentication works. If DNS issues persist, try using a different DNS server. You can also contact your internet service provider for assistance. Clear your DNS cache. Then, restart your network adapter. This can fix temporary connectivity issues.
Performance Issues
Experiencing slow speeds or dropped connections with Mount Sinai VPN? Discover quick fixes to boost performance and ensure a stable, secure connection.
Slow Connection Speeds: VPNs can slow down your connection. If speeds are very slow, it may indicate configuration issues or network congestion. Check your base internet speed without a VPN to set a baseline. Then, compare it to your speed with the VPN. This helps find any problems.
Server selection significantly impacts connection speed. Choose Mount Sinai VPN servers geographically closest to your location for optimal performance. Choose servers with lower utilization rates if your VPN shows server load info. This can improve speed and reliability.
Background applications consuming bandwidth can severely impact VPN performance. Close unneeded programs, pause automatic updates, and limit streaming or downloads. This will help improve performance when using Mount Sinai systems.
Intermittent Disconnections: Unstable VPN connections often happen because power management settings put network adapters to sleep. Turn off power management for your network adapter. On Windows, do this in Device Manager. For Mac, go to Network Preferences. This helps keep your connection steady.
Wi-Fi connections are particularly prone to intermittent disconnections. Use wired Ethernet connections for stable VPN access. This is especially important when using critical healthcare applications or handling patient data. Uninterrupted connectivity is key.
DNS Resolution Problems: DNS issues can make websites and Mount Sinai resources load slowly or not load at all. Set up your VPN client to use Mount Sinai DNS servers for internal resources. Also, keep backup DNS options for external internet access.
Clear your DNS cache often. This stops old DNS info from causing issues with resolution.
To fix connectivity issues, use command-line tools. On Windows, type “ipconfig /flushdns.” For macOS, use “sudo dscacheutil -flushcache” to clear the DNS cache.
Platform-Specific Issues
Facing VPN glitches on Windows, macOS, or mobile? We’ll guide you through tailored solutions to resolve platform-specific Mount Sinai VPN issues fast.
Windows Troubleshooting: Windows Defender or third-party antivirus software can interfere with VPN connections. Add your VPN client to the antivirus exclusion list. Also, check that real-time protection isn’t blocking the VPN traffic.
Windows Updates can sometimes cause VPN compatibility issues. This may need driver updates or upgrades to the client software.
Network adapter driver problems can cause persistent connection issues on Windows systems. Update network drivers in Device Manager. If issues continue, reinstall the VPN client.
Mac Troubleshooting: macOS security features, such as Gatekeeper, may prevent VPN clients from functioning correctly. Check System Preferences > Security & Privacy. Make sure your VPN client is approved to run. macOS updates sometimes require VPN client updates for continued compatibility.
Keychain issues can cause authentication problems on Mac systems. Verify that VPN credentials are stored correctly in Keychain Access and remove any duplicate or corrupted entries that might interfere with authentication.
Mobile Device Issues: Battery optimization features on mobile devices can limit background app activity. This may cause problems with VPN connectivity. Disable battery optimization for your VPN app to ensure a consistent connection.
Mobile data restrictions or carrier-specific VPN blocking can prevent successful connections. Connect to Wi-Fi to see if cellular restrictions are causing issues. If VPN access is still blocked, contact your mobile carrier.
Advanced Troubleshooting Techniques
If standard troubleshooting doesn’t fix your Mount Sinai VPN issues, try advanced diagnostic techniques. They can help find and solve more complex problems. These methods need some technical know-how. However, they can be very helpful for ongoing connection issues.
Network Diagnostics Tools and Commands
Network diagnostic commands give clear details about your connection status. They help find specific issues. On Windows, use the “ping” command. This will check your connection to Mount Sinai VPN servers and ensure your network path is clear. The “tracert” command shows the path your connection takes. It helps identify where delays or failures happen.
Use “nslookup” to check DNS resolution for Mount Sinai domains. This ensures that internal resources resolve properly. This command helps distinguish between authentication problems and DNS issues. Both can show similar symptoms.
On Mac and Linux, you can use commands like “ping,” “traceroute,” and “nslookup.” They give you similar diagnostic information. The “netstat” command displays active network connections. It helps find conflicting applications or services.
Advanced users can use tools like Wireshark to capture and analyze VPN traffic. However, this needs technical skills, so it’s best to consult Mount Sinai IT support to avoid breaking security policies.
Firewall and Antivirus Configuration
Firewall configurations can significantly impact VPN connectivity, particularly in corporate environments or homes with sophisticated security setups. Document your current firewall rules first. Then, make specific exceptions for Mount Sinai VPN traffic.
Common VPN ports that might need firewall exceptions are:
- UDP 1194 for OpenVPN
- UDP 500 and 4500 for IKEv2
- TCP 443 for SSL VPN connections
Check with Mount Sinai IT services for the specific ports and protocols used by their VPN.
Antivirus software with network protection can disrupt VPN connections. It may scan or block encrypted traffic. Set exceptions for your VPN client in the antivirus software. You may also try temporarily disabling real-time protection to see if it’s causing connection issues.
Port Forwarding Requirements
Some network setups need port forwarding for VPN connections. This is especially true if you’re behind strict firewalls or NAT devices. Find out the specific ports for Mount Sinai VPN services. Then, set up your router to forward these ports to your device.
UPnP (Universal Plug and Play) can set up port forwarding automatically for VPN apps. However, this feature might be off on secure networks. Check your router’s UPnP settings and enable them if your network security allows it.
Certificate and Authentication Issues
Certificate problems can lead to authentication failures, even with correct credentials. Check your system’s certificate store for expired or corrupted Mount Sinai certificates. Update them if needed. Certificate validation errors may also signal time sync issues, so ensure your system clock is accurate.
For advanced troubleshooting, examine certificate chains and trust relationships to identify potential issues. This ensures proper authentication. Use certificate management tools to verify that all required intermediate certificates are installed and configured correctly.
Contacting IT Support: When and How
Know when to reach out to the Mount Sinai IT helpdesk instead of trying to troubleshoot on your own. Contact support right away for ongoing authentication issues, suspected security breaches, or hardware connectivity problems.
Before contacting technical support, gather as much detailed information as possible. Include error messages, troubleshooting steps you’ve tried, and details about your device and network setup. This helps support staff quickly pinpoint and fix your issue.
Keep track of support ticket numbers and resolution steps for future reference. Record recurring issues and their solutions. This builds your troubleshooting knowledge and may help spot patterns that show underlying problems.
Security Best Practices
Maintaining strong security with Mount Sinai VPN is key to protecting healthcare data and meeting HIPAA rules. Following security best practices ensures that your remote access to Mount Sinai systems remains safe and compliant with healthcare industry standards.
Password Management for VPN Access
Strong password practices are essential for secure VPN access. Create unique, complex passwords for your Mount Sinai network account. Use a mix of uppercase and lowercase letters, numbers, and special characters. Avoid personal information or common words that malicious actors could easily guess.
Use a password manager to securely generate and store strong passwords. This lets you maintain complex, unique passwords without the risk of forgetting them. It also helps you avoid insecure methods, like writing them down. Many popular password managers offer secure sharing features for healthcare teams to manage shared account credentials safely.
Change your VPN password regularly, in accordance with Mount Sinai IT policy. Typically, you should update it every 90 days or as specified by your organization’s security guidelines. Never share your VPN credentials with colleagues or store them in unsecured locations, such as email or text files.
Multi-Factor Authentication Setup
Configure and maintain your Symantec VIP Access app for reliable two-factor authentication. Ensure your mobile device’s time is synchronized with the network time servers. This helps prevent timing issues with authentication codes. Use the app’s backup features to save your VIP Access credentials. This way, you won’t get locked out if you lose or replace your device.
Also, consider using extra authentication methods when possible. Hardware tokens or biometric authentication add an extra layer of security. These methods help protect against credential theft and unauthorized access attempts.
Safe Browsing While Connected
Be careful when browsing the internet on the Mount Sinai VPN. Avoid visiting suspicious sites and downloading files from untrusted sources. These actions could put the hospital network at risk. Stay as vigilant as you would when in Mount Sinai facilities.
Use secure, encrypted connections (HTTPS) whenever possible on external websites with the VPN. This provides additional protection for your data and helps prevent man-in-the-middle attacks.
Avoiding Public Wi-Fi Risks
VPNs encrypt your data, but public Wi-Fi still poses security risks. Be careful when using it. Avoid accessing sensitive patient information or critical healthcare systems on public networks, even when using a VPN.
Choose reputable Wi-Fi networks in public places. Avoid networks with generic names or those that lack passwords. Hotel and coffee shop Wi-Fi networks that require authentication are usually safer than open ones.
Regular Software Updates
Keep your VPN client software up to date with the latest security patches and features to ensure optimal performance and security. Enable automatic updates or check for them regularly to protect against known vulnerabilities.
Update your operating system and other security software often. Outdated software can create weaknesses that compromise VPN security, even if the connection is encrypted.
Frequently Asked Questions
Who is eligible for Mount Sinai VPN access?
Mount Sinai VPN access is available to employees, faculty, students, and authorized contractors who require remote access to hospital systems and resources. Eligibility rules may differ by department and role. Please contact Mount Sinai IT Services to check your access and start the account setup process.
How do I request VPN access?
New users should contact their department’s IT liaison or the Mount Sinai IT Helpdesk for VPN access. This process typically involves completing security training and explaining the necessity of remote access in relation to job duties.
What devices are compatible with Mount Sinai VPN?
The VPN service works with Windows, Mac, iOS (iPhone and iPad), and Android devices. Check specific version requirements to ensure compatibility before installing.
Can I use the VPN on multiple devices?
Most Mount Sinai VPN setups let users install the client on multiple devices. However, there may be limits on the number of simultaneous connections. Check with IT services to know your specific connection rules.
How many simultaneous VPN connections are allowed?
Connection limits vary depending on the user’s type and departmental policy. Most individual users have one or two simultaneous connections. Some roles may have different limits based on job needs. Contact IT support if you need more concurrent connections.
What happens if I exceed connection limits?
Exceeding your connection limit usually disconnects the oldest connection when a new one is made. Plan your use of multiple devices to avoid unexpected disconnections.
Are there restrictions on the locations where VPN usage is permitted?
Mount Sinai VPN can be used from most places with internet access. However, some geographic or network restrictions may apply. If you are traveling internationally, you may need special approval for VPN access.
Can I use a VPN from other countries?
International VPN usage may be restricted due to regulatory or security considerations. Contact IT support before traveling internationally if you need VPN access while abroad.
How do I contact Mount Sinai IT support?
The Mount Sinai IT helpdesk provides technical support for VPN issues through multiple channels, including phone support, email tickets, and online chat systems. Please check the Mount Sinai intranet or employee portal for the most up-to-date contact information and support hours.
What information should I provide when requesting support?
Prepare detailed information, including error messages, device type, operating system, network location, and troubleshooting steps already attempted. This information helps support staff quickly diagnose and resolve your specific issue.
Conclusion
Successfully accessing Mount Sinai systems through VPN requires understanding both the technical setup process and security best practices that protect healthcare data. This comprehensive Mount Sinai VPN guide covers essential topics, from initial installation to advanced troubleshooting, providing healthcare professionals with the knowledge needed to maintain secure and reliable remote access to critical hospital systems.
The key to successful VPN usage lies in following proper procedures for setup, authentication, and ongoing maintenance. Regular software updates, strong password practices, and proper multi-factor authentication setup form the foundation of secure remote access. When problems arise, systematic troubleshooting using the techniques outlined in this guide can resolve most common connectivity issues.
Remember that VPN security extends beyond technical configuration to include safe browsing practices and awareness of network security risks. Healthcare professionals have a special responsibility to protect patient data and maintain HIPAA compliance even when working remotely, making proper VPN usage an essential component of modern healthcare delivery.